문서의 이전 판입니다!
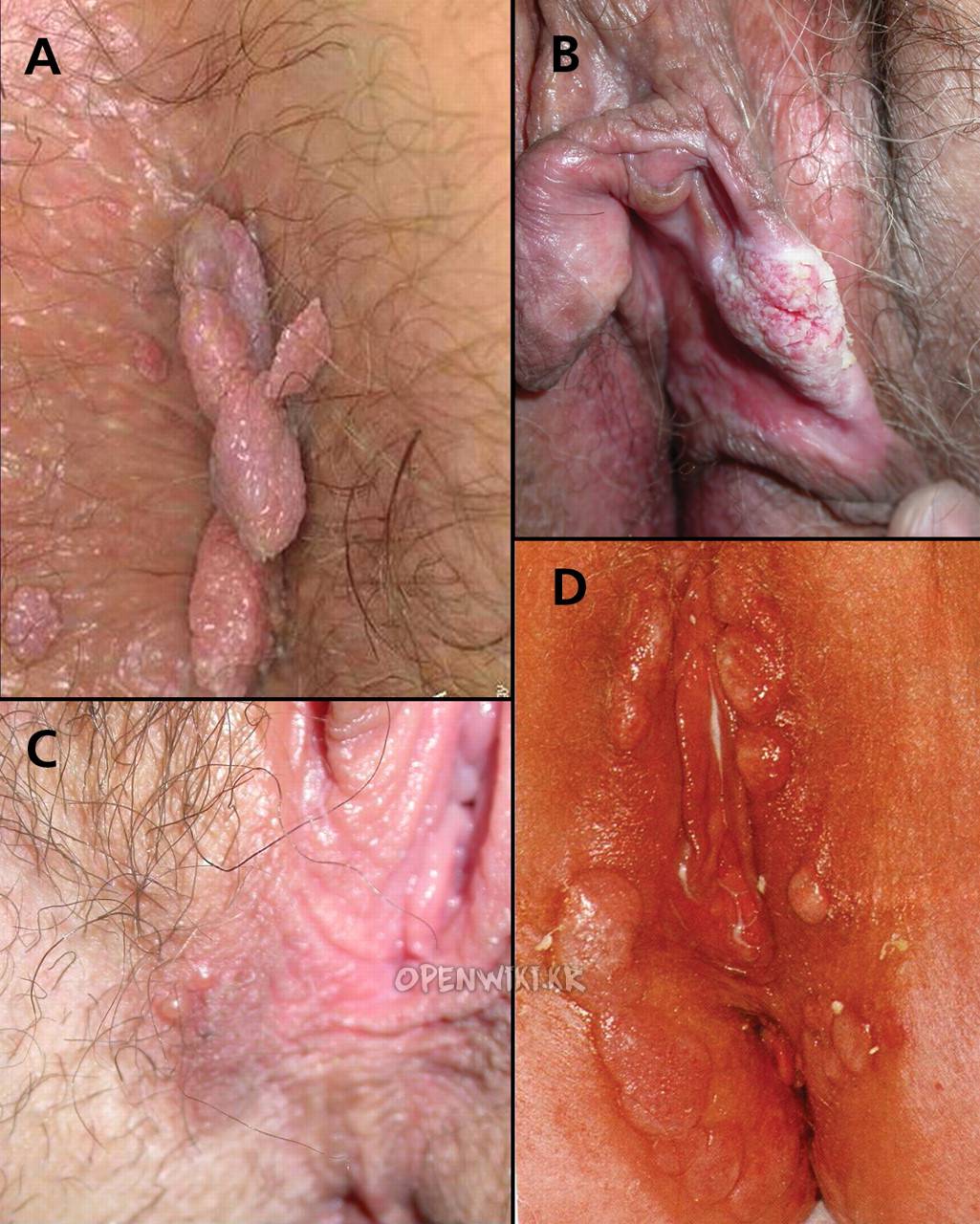
질전정유두종증 [Vulvar Vestibular Papillomatosis]
Vulvar vestibular papillomatosis is an anatomical variant of the vulva. In a prevalence study in London, UK, one per cent of women showed vestibular papillomatosis. Other authors found prevalence rates between 5.1 to 33%.
The visible lesion of vestibular papillomatosis may be a nonspecific response to discharge or inflammation.
Vestibular papillae are hard to distinguish from genital warts with just a visual inspection, but there are a few differences between the two conditions. Vestibular papillae appear in a symmetrical configuration, and are usually arranged in lines, while genital warts seem to be random. Warts are firm in texture, and pink, red and white in color. Vestibular papillae are the same color as nearby mucosal tissue and soft in texture. Vestibular papillae all have separate basis, while warts tend to have small projections coming from just one base.